25G PON
25G PON
25G PON is realizing new services and applications through the same optical fiber access network as GPON and XGS-PON. Some operators are deploying 25G PON to support small cell xHaul transmission based on PON-based point-to-multipoint fiber-optic efficient topology. 25GS-PON MSA (Multiple Source Agreement) group composed of many suppliers and operators. This MSA focuses on technical specifications such as optics and ensuring coexistence with GPON and 10G GPON.
Nokia provides 25G PON support to operators in Europe, North America, and some countries in Asia and Oceania. Nokia also plans to support 50G PON. Nokia believes that both 25G PON and 50G PON have opportunities. Meanwhile, Nokia has developed its own PON MAC ASIC, which currently supports GPON, 10G PON, and 25G PON.
In contrast, Huawei is not pursuing the 25G PON opportunity, nor are its largest telecom customers, such as China Mobile and China Telecom. Chinese operators have no plans to use 25G PON to support 5G small cell xHaul transport or support any wholesale or open access strategy. However, Chinese operators are very interested in adopting 50G PON as the next major upgrade to their 10G PON networks. Huawei is developing 50G PON. It also has internal self-developed chip design capabilities and is expected to realize the development of 50G PON MAC ASIC.
cost-effectiveness is key
There are two requirements for the success of access technologies: cost-effectiveness and market demand. In large-scale access network deployment, the former is the key. 25G PON has the following advantages:
VO-band wavelength
The higher the bit rate, the higher the dispersion. The upstream and downstream wavelengths of 25G PON are all in the O-band, which can avoid large losses or the need for dispersion compensation.
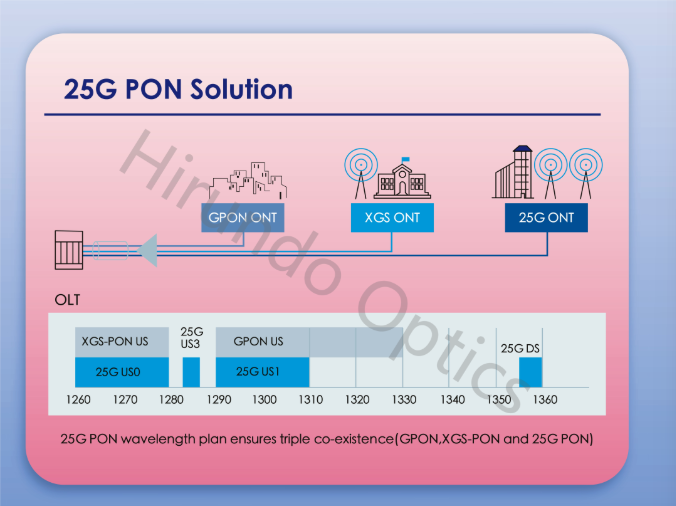
The 25G-PON standard specifies the downstream 1358 nm wavelength and three upstream options:
²Option 1: 1300 nm (a subset of GPON) coexists with XGS-PON.
²Option 2: 1270 nm (same as XGS-PON) coexists with GPON.
²Option 3: 1286 nm, support triple coexistence of 25G PON, XGS-PON, and GPON
This choice of wavelength plan ensures a smooth evolution path in any network.
Transmission
While utilizing data center technology, 25G PON does not require all the functions required by data centers. It can use simple non-return-to-zero (NRZ) transmission instead of higher-level, costly modulation schemes like PAM4.
Optical magnification
Compared with 10 Gb/s, the power loss of 25 Gb/s is about 5 dB. To achieve a loss budget of 29 dB (PR30 EPON, N1 class ITU-T PON) and avoid the cost of optical amplification, these 5 dB need to come from a combination of higher transmit power, better receiver sensitivity, and stronger FEC. It would be possible, but not with much margin.
Dual rate transmission
25G PON supports both symmetric (25/25) and asymmetric (25/10) bit rates. This enables the use of lower-cost 25G/10G ONTs where symmetry is not required.
25G PON is the most effective way to evolve fiber optic networks to the next generation, a simple technology that uses a single wavelength and does not require tuned lasers. It can coexist with GPON and XGS-PON and provide a higher 25 Gb/s downstream rate and a 25 Gb/s or 10 Gb/s upstream rate. It is also based on proven optical technology and a growing ecosystem, enabling the technology to be brought to market faster. It can meet the needs of higher density residential, commercial, etc. in the short term, while dealing with the competitive threats of 25G EPON and cable TV operators.

