A new level of WDM: Detailed explanation of Ethernet colored light solution
A new level of WDM: Detailed explanation of Ethernet colored light solution
1. Discover the secrets of colored light technology
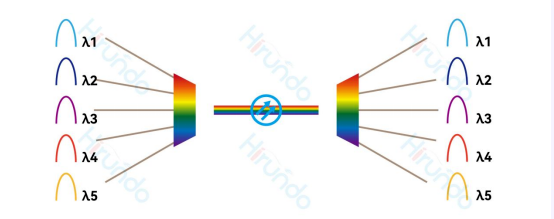
Colored light technology (WDM) refers to wavelength division multiplexing technology in the field of optical communications.
It is a technology that can transmit multiple optical signals of different wavelengths through the same optical fiber.
Each wavelength signal carries an independent information stream.
thereby achieving multiplexing and increasing the transmission capacity of the optical fiber.
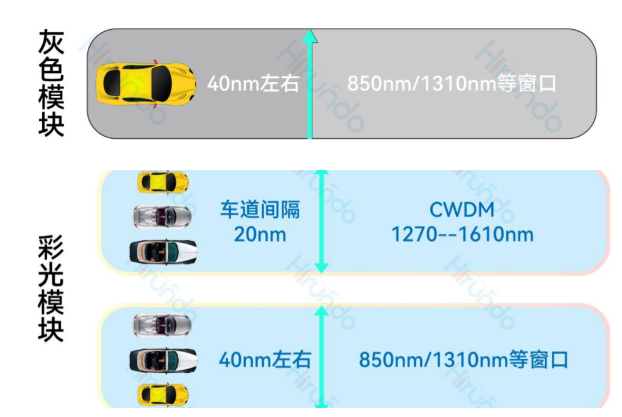
2. The difference between gray light and colored light
|
Gray light |
Colored light |
|
|
wavelength |
Usually located at 850 nm and 1310 nm, there is no specific standard wavelength for the optical signals in these two bands. |
Specifically refers to the optical signal located at 1550 nm. The optical signal in this band has a standard wavelength. |
|
characteristic |
The optical signal of gray light fluctuates within a certain range. It has no fixed center wavelength and is a wide range. |
The optical signal of colored light fluctuates within a small range near a certain central wavelength and is highly stable and consistent. |
|
follow standards |
ITU-T G.957, G.957, ITU-T IEEE 802.3 |
ITU-T G.694.1 (DWDM) and ITU-T G.694.2 (CWDM) |
|
application |
Gray light is usually used in SDH (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy), IP, and other networks, and is suitable for short-distance transmission scenarios |
Colored light is widely used in OTN (Optical Transport Network) and other networks and is suitable for long-distance transmission scenarios. |
The reason why colored light technology is chosen to apply colored light instead of gray light is mainly because colored light technology has significant advantages in transmission capacity, transmission distance, technical standards and compatibility, and application scenarios. These advantages make colored light technology one of the important technologies in the field of modern optical communications.
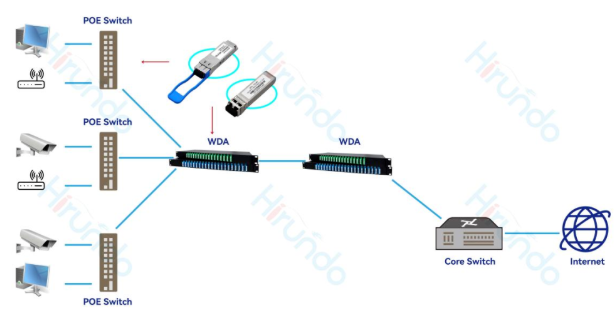
3. Hirundo Ethernet all-optical 3.X solution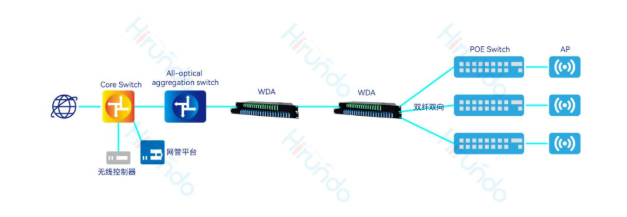
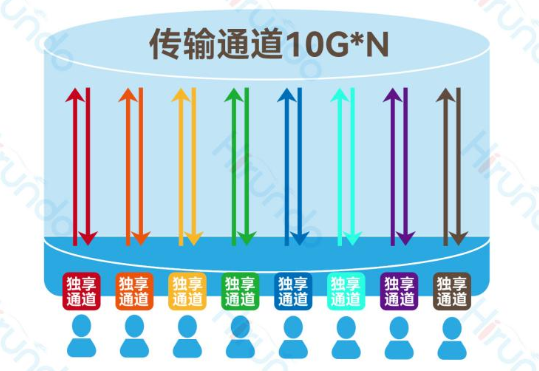
Hirundo Ethernet all-optical 3. Ethernet-colored light also uses optical fiber as the transmission medium. But the protocol relies on Ethernet and combines and splits waves through WDM technology, so that different optical signals can be transmitted on a backbone optical fiber, which is a point-to-point exclusive mode. There is no light splitting at the optical path level, and the transmission efficiency is increased by 8 times.
The core computer room deploys super-aggregated switches, downlink passive colored optical equipment, and all-optical access switches are deployed in each room through fiber optics. The aggregation nodes are completely passive, and the weak current room has zero maintenance. It is also a 2-layer architecture.

Hirundo Ethernet Color Light Solution
Hirundo's Ethernet color optical solution combines a series of optical signals carrying information but with different wavelengths into a single beam through WDM and transmits them along a single optical fiber. At the receiving end, the same technology is used to separate the optical signals of different wavelengths. This technology can simultaneously transmit multiple signals on a single optical fiber. Each signal is transmitted by light of a specific wavelength, and the light of different wavelengths does not interfere with each other. Each wavelength transmits signals independently at the same time; thus, there is no loss in transmission bandwidth.
5. The method for converting between the Ethernet color light solution and the Ethernet All-light 3.X solution